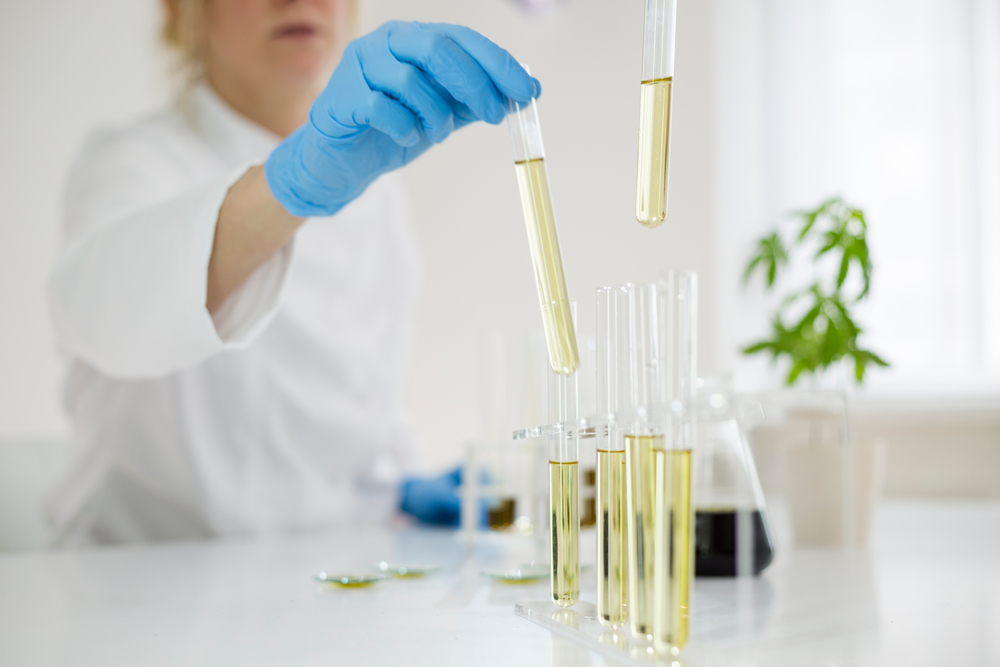
Cannabis users have a number of options in terms of how they consume. They can smoke cannabis flower or dry heat it in a specialized vaporizer. They can ingest it by adding it to recipes. Users who do not want to directly consume plant material can purchase a cannabis-derived product like a vape cartridge, tincture, or topical lotion. Making derived products requires extracting cannabinoids and terpenes from plant material.
Thanks to the highly competitive nature of the industry, extraction is a real science these days. Houston-based extraction equipment manufacturer CedarStoneIndustry says companies invest tens of thousands of dollars – if not more – in tanks, extractors, etc.
Processors design their processing lines around the particular extraction method they have chosen. Needless to say, they have choices. There are lots of ways to extract cannabinoids from plant material, including the five described below. Each has its advantages and disadvantages.
-
1. Butane Extraction
Solvent extraction utilizing a chemical solvent is arguably the most common extraction method in the U.S. One of the solvents used is butane, an alkane and one of the many natural gases found in petroleum products. It is liquefied prior to being used for plant extraction.
Extracting with butane is a fairly straightforward process. Plant material is saturated with butane in a temperature-controlled, pressurized chamber. As plant material dissolves, processors are left with a resin consisting of cannabinoids, terpenes, and other chemical compounds. That resin is separated from the butane by allowing the gas to evaporate at room temperature. Butane extraction yields a resin with about 80% concentration.
-
2. Ethanol Extraction
Ethanol extraction is similar to butane extraction except for the solvent being use. Ethanol is considered generally safe by the FDA. Furthermore, it is utilized for other extraction processes above and beyond cannabis. Regardless, plant material is soaked in ethanol where it begins to dissolve. The resulting resin is then processed to enhance its purity.
-
3. Supercritical CO2 Extraction
Although supercritical CO2 acts as a solvent on cannabis plant material, this particular extraction method is viewed as separate from solvent extraction because it doesn’t utilize any chemicals. Rather, CO2 is liquefied by cooling it and maintaining it at a constant temperature and pressure. It is then injected into a pressurized chamber where plant material has already been placed. The supercritical CO2 dissolves the plant material, leaving the resin behind.
-
4. Isopropyl Extraction
A lesser used form of chemical solvent extraction involves isopropyl alcohol. Plant material is soaked in the alcohol to loosen it up. Plants are then shaken to encourage the trichomes to fall off. The trichomes are soaked a little while longer to break them up before the entire mixture is sent through a series of filters to eliminate any remaining plant material and isolate the desired chemical compounds.
-
5. Water Extraction
The final method on our list, water extraction, should not be confused with steam distillation. Water extraction subjects plant material to freezing water in order to separate trichomes from the rest of the plant material. The trichomes are then stirred in the freezing water a while longer before the mixture is filtered to isolate the desired chemical compounds. While this may be the easiest way to extract cannabinoids, it yields the lowest volumes at between 50 and 70%.
Regardless of the chosen extraction method, processors follow up by further processing extracts in order to isolate certain cannabinoids and terpenes. There is a lot of science involved. Because they are able to do it, processors can create all sorts of cannabis-derived products including infused foods, gummies, and topical lotions.