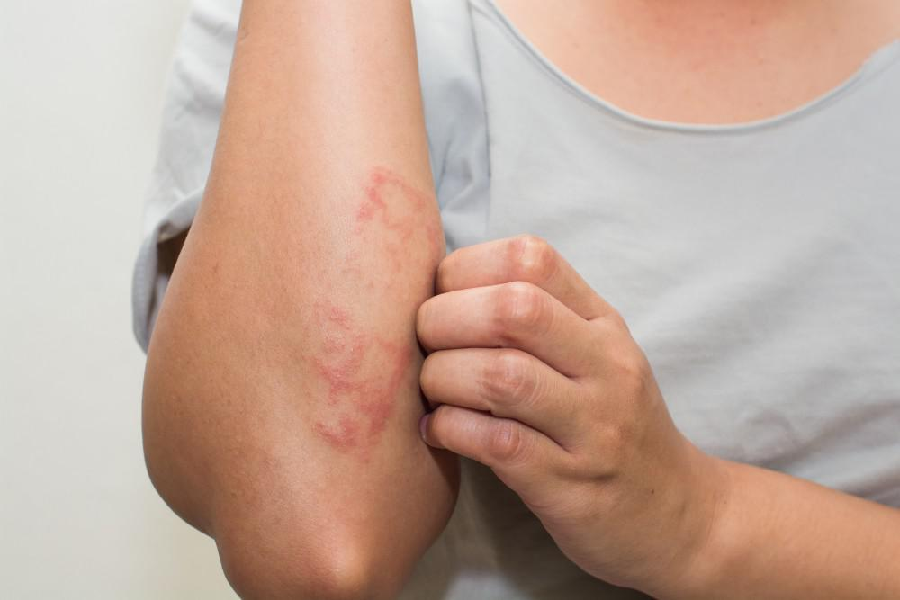
Eczema(ekzema)is commonly known as a skin condition caused by inflammation of the skin. The common age group to suffer eczema are infants and children, although some might experience these symptoms for lifelong. This skin condition usually starts from the face, elbow, behind the knees and elsewhere. The most common symptom of eczema is itchiness and redness of the skin affected.
It usually starts with blisters on inflamed skin and eventually breaks releasing fluids from inside. For chronic eczema, blisters are usually not seen but skin often becomes thick and pale.
Prevention of eczema
Prevention is better than cure. Eczema can be prevented by keeping your children always in a cool room and by avoiding a hot bath and overdressing the child especially with rough clothes. Avoid your child from contacting scratchy fabric and identify for possible food allergy and consult a doctor for further evaluation. Lotion creams are usually used to keep the skin always moist and from exposing to allergens.
As stress can be a triggering factor for exacerbation of eczema, you can practice breathing exercise, yoga, meditation and listening to soothing music and focus on sleep hygiene.
Treatment of eczema
Eczema can be treated medically by consuming topical and systemic medications. Commonly these medications are prescribed by doctors for kids with eczema.
- Hydrocortisone cream. Hydrocortisone cream contains an appropriate amount of steroid to help combat the inflammation that has been causing the blisters on exposed skin. Over the counter cream with 1% are usually available to be used for eczema condition. However, it should be used with caution as it can cause side effects if used for a prolonged period.
- Antihistamine is usually prescribed in oral or systemic form to stop and reduce the inflammation on the skin. Antihistamine works by prevention fighter cells in our body from releasing the chemical histamine that is responsible to aggravate inflammation.
- Topical immunomodulators, (TIM). This medication is prepared as cream and function to suppress the inflammatory cells in our body.
- In some conditions, your doctor might prescribe you with antibiotics to curb the microorganisms causing the eczema. These antibiotics have to be taken according to the prescribed duration and frequency without missing to prevent the development of bacterial resistance.
- Cyclosporine is commonly known as an immunosuppressant and usually spared for the last resort to treat eczema if any of these above medications does not help to reduce the flare and inflammation.
Type of eczema
There are several types of eczema that commonly happens in children. It will be further discussed below.
- Atopic dermatitis. This condition is usually inherited and it is the most common type of eczema in children and adults.
- Irritant dermatitis. This type of condition occurs when the skin is frequently exposed to chemicals that are possible to irritate the skin.
- Stasis dermatitis. Most commonly occurs for patients with venous problems in their legs. Areas that are swollen due to poor venous circulation are prone to have stasis dermatitis.
- Seborrheic dermatitis. This condition causes inflammation to skin at head, face, ears and chest in adults.
Conclusion
Eczema is a very common skin disease seen in general practice and commonly known as atopic dermatitis. It is usually seen as patches of dry, itchy and thickened skin at the areas of hands, face, neck and legs as well. Sometimes, blisters that ooze fluids are also formed on these exposed skins.
The best way to manage eczema is by preventing it from becoming worse. Triggering factors such as viral infections, soaps, detergents, perfumes and fabric clothes should be avoided at any cost. Furthermore, food that aggravates eczema also should be avoided.